Continuous Localization: The Future of Global Product Delivery
Global digital economy, software products, websites, and apps evolve rapidly. Agile development cycles and continuous delivery have become the norm, enabling teams to push out updates multiple times a week – or even daily. However, as products reach international audiences, the need to localize content regularly and efficiently has become a major challenge. Traditional localization processes, often managed manually and asynchronously, are no longer sustainable in this fast-paced environment.
Enter continuous localization – a modern approach that integrates localization directly into the development and deployment pipeline. It transforms localization from a bottleneck into a seamless, automated process that keeps pace with product development. For global-first companies, continuous localization is now fundamental to delivering high-quality, multilingual experiences without slowing down innovation.
What is continuous localization
So, what is continuous localization?
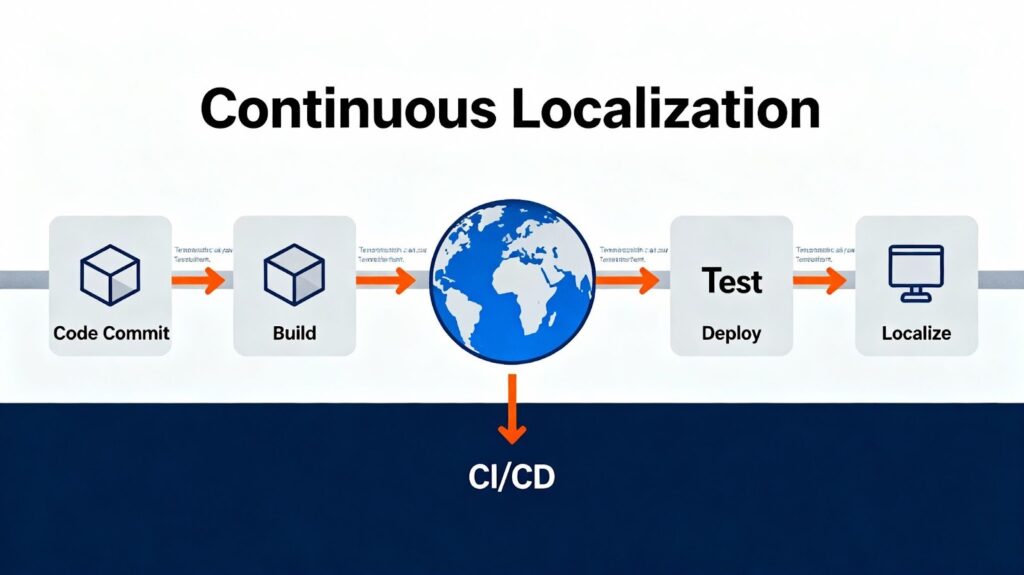
Continuous localization is a modern, automated workflow in which product content is translated, reviewed, tested, and deployed continuously – often in real time – as developers update or release new features. Instead of sending large translation batches every few months, continuous localization integrates directly with the product’s codebase, CMS, or content pipeline, allowing translations to happen automatically whenever new or updated content is detected.
At its core, continuous localization turns localization into an uninterrupted cycle that matches agile development practices. It enables teams to:
- Translate strings as soon as they are created
- Automatically sync localization files between repositories, translation platforms, and apps
- Visualize translations in context before launch
- Run automated QA checks across all languages
- Deploy multilingual content instantly as part of CI/CD workflows
This approach eliminates the historical disconnect between development and localization by making translation a native component of the product lifecycle – not an optional, time-consuming add-on.
Continuous localization is powered by:
- Localization management platforms (e.g., Crowdin, Phrase, Lokalise)
- Automation through APIs, webhooks, CLI tools
- Machine translation + AI-assisted workflows for speed
- In-context editing to reduce errors
- Version control integration (GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket)
For globally focused companies, continuous localization is no longer a luxury – it’s the operational foundation needed to scale efficiently.
How Continuous Localization Works
Continuous localization relies on technology integration, automation, and communication between developers, translators, and localization managers. Below is an overview of how the process typically works within a modern software development environment.
1. Integration with Development Tools
The first step involves connecting localization systems with the tools that developers use daily, such as GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket, or Azure DevOps. This integration ensures that new or modified source files are automatically detected when developers commit changes to the repository. APIs or plugins then extract translatable text (strings) from the codebase and send it to the localization system.
2. Automated String Extraction
In traditional workflows, teams manually collect and send translation files to localization vendors – a time-consuming and error-prone process. Continuous localization automates this step completely. Whenever new strings appear in the codebase, they are instantly flagged, extracted, and sent to the TMS. This automation minimizes lag time and reduces the risk of missing content.
3. Translation Management and Workflow Automation
Once the new content is detected, the translation management system assigns the strings to translators, machine translation engines, or both. Translators can work on them immediately in an online interface with built-in translation memory, terminology databases, and quality assurance checks.
For repetitive or previously translated content, the TMS reuses existing translations, ensuring consistency and reducing costs. Machine translation (MT) can speed up the process for frequent updates, with human linguists reviewing critical sections to maintain accuracy and tone.
4. Review and Quality Assurance
After translation, automated QA checks verify that the localized content adheres to format rules, maintains placeholders, and fits UI constraints. Reviewers can preview how the translations appear within the product’s layout using dynamic previews, minimizing visual errors or truncation issues.
5. Automatic File Synchronization and Deployment
Once the translations are approved, the system automatically pushes the localized files back into the code repository. From there, continuous delivery pipelines handle deployment, ensuring users worldwide receive the updated content within minutes. Depending on the setup, this process can happen multiple times per day.
6. Feedback and Continuous Improvement
Continuous localization thrives on omnidirectional feedback. Translators, developers, and QA testers collaborate more closely because the workflow is connected through real-time dashboards and notifications. Over time, the system learns from user feedback, developer adjustments, and linguistic reviews to continuously refine output quality.
7. Analytics and Monitoring
Advanced continuous localization systems provide analytic dashboards that display metrics such as translation progress, turnaround times, rework rates, and QA results across languages. These metrics empower teams to identify bottlenecks, optimize vendor performance, and improve automation efficiency.
Overall, continuous localization brings developers, translators, and automation into a single, unified loop – ensuring that global product updates are timely, accurate, and consistent.
Key Benefits
Implementing continuous localization can dramatically transform how a company approaches product development and global expansion. Below are the major benefits that make this approach a cornerstone for modern SaaS platforms, digital products, and global businesses.
1. Real-Time Global Releases
The most powerful benefit of continuous localization is synchronized global releases. Since localization occurs in parallel with development, international users no longer have to wait weeks or months for translated versions. Whether launching a new feature or updating UI content, all users across markets have access simultaneously, ensuring global brand consistency.
2. Faster Time-to-Market
Continuous localization eliminates manual handoffs and delays that traditionally slow down localization. With automation driving the workflow, businesses can reach new markets faster, outperform competitors, and accelerate product launch cycles without sacrificing quality.
3. Improved Workflow Efficiency
By automating repetitive tasks such as string extraction, file exchange, and translation updates, teams can focus on higher-value activities like contextual translation, quality assurance, and user experience improvements. The efficiency gains are especially visible in agile teams that release updates frequently.
4. Cost Reduction
Automation reduces human errors and rework while optimizing translator workloads via translation memory and machine translation integration. Over time, these efficiencies lead to significant cost savings. Additionally, small incremental updates cost less to localize compared to large, irregular translation batches.
5. Consistent User Experience
Continuous localization ensures that all markets receive the same level of quality and attention in each update. This consistency strengthens the brand image and enhances customer satisfaction, promoting trust among international users.
6. Seamless Integration with CI/CD Pipelines
Continuous localization naturally complements continuous integration and deployment systems. By integrating with DevOps workflows, localization becomes a routine part of software iteration rather than a separate, reactive process. This reduces friction between engineering and localization teams and ensures smooth global rollouts.
7. Enhanced Collaboration and Transparency
Modern continuous localization platforms provide collaboration tools that connect developers, translators, and product teams in real time. Translators have immediate access to context, screenshots, and comments, leading to better-quality outputs. Managers can track progress through dashboards, ensuring full transparency of the localization process.
8. Quality at Scale
Quality assurance is built into every stage of continuous localization. Automated checks, linguistic QA, and real-time previews help detect issues before they reach production. Because localization occurs continuously, teams can identify and correct problems early, maintaining high linguistic and visual quality even at scale.
9. Scalability for Growing Teams and Markets
As businesses grow and add new markets, continuous localization scales effortlessly. Whether you’re adding one language or twenty, the underlying automation handles updates uniformly across all regions. This scalability is essential for SaaS, e-commerce, and gaming companies expanding into multiple territories.
10. Enhanced Cultural Adaptation
Continuous localization makes it easier to adapt brand messaging, tone, and UX for different audiences. By localizing continuously, marketers and product designers can test cultural nuances regularly, ensuring that the product resonates authentically in every region.
FAQs About Continuous Localization
What is the difference between traditional localization and continuous localization?
Traditional localization operates on a project basis – translation happens after development, causing delays and version mismatches. Continuous localization, on the other hand, integrates localization into ongoing development workflows. This allows teams to push updates and translations simultaneously, enabling real-time global releases.
Is continuous localization only for large enterprises?
Not at all. While large enterprises adopted the concept early, continuous localization is now accessible to organizations of all sizes, thanks to affordable cloud-based tools. Even startups with small teams can benefit from automation and real-time updates to streamline their internationalization strategy.
How does continuous localization relate to agile development?
Agile development focuses on iterative releases, which means software changes frequently. Continuous localization aligns perfectly with this methodology – translations are updated continuously alongside development, ensuring localized versions are always in step with the latest product iteration.
What role does machine translation play in continuous localization?
Machine translation (MT) plays a supportive role by handling repetitive or straightforward updates quickly. In continuous localization systems, MT engines can automatically translate newly added strings, which are then reviewed by human linguists for quality. This hybrid approach combines speed with accuracy.
What tools are used for continuous localization?
Common tools include Translation Management Systems (TMS) like Crowdin, Lokalise, Phrase, Smartling, and Transifex. These platforms connect directly to version control systems, CI/CD pipelines, and automation frameworks, enabling end-to-end management of localization tasks.
How can a company implement continuous localization?
Implementation generally involves connecting your code repositories (like GitHub or GitLab) to a TMS platform via APIs or plugins. The next step is defining workflows for translation, review, and deployment, followed by testing automation steps. It often starts small – with one or two languages – and scales progressively as efficiency improves.
How do teams maintain linguistic quality in continuous localization?
Quality is maintained through translation memories, style guides, term bases, and automated QA checks. Linguists review context-aware translations using in-platform previews. Regular audits and feedback cycles further enhance quality over time.
Is continuous localization suitable for all content types?
While continuous localization is ideal for digital products, UI elements, and software documentation, it’s less effective for large creative projects like novels or marketing campaigns that require deep contextual analysis. However, even for marketing platforms, certain repetitive content can still benefit from automated localization workflows.
What are the biggest challenges in adopting continuous localization?
Common challenges include initial setup complexity, aligning engineering and localization teams, and training translators to use new tools. Overcoming these challenges requires a strategic approach, focusing on process education and technology familiarization.
How does continuous localization impact user experience?
Continuous localization ensures that users around the world receive updates and improvements at the same time, maintaining consistent experiences. It also allows teams to respond faster to market feedback, adjust translations, and fix cultural issues dynamically, resulting in a truly global and user-centered experience.
Does continuous localization eliminate human translators?
Not at all – it enhances their effectiveness. While automation handles repetitive tasks, human linguists focus on higher-level quality control, editing, and cultural adaptation. Machines manage speed and efficiency, humans preserve nuance and authenticity.
Can continuous localization handle multimedia content?
Yes, advanced systems can manage multimedia elements such as subtitles, images with embedded text, and video captions. Automated extraction tools identify translatable elements while localized versions are uploaded and synced automatically.
Conclusion
Continuous localization represents a strategic evolution in how global software and content teams operate. By marrying automation with human creativity, it ensures that localization keeps pace with rapid product updates, user expectations, and market expansion. Instead of being a reactive afterthought, localization becomes a proactive, embedded part of the development process – a silent engine driving global success.
For companies aspiring to succeed globally, adopting continuous localization is no longer optional; it’s a competitive necessity. It ensures that every new feature, fix, and message reaches users everywhere – simultaneously, seamlessly, and in their own language.


